The Impact of Hearing Tests on Quality of Life
Regular hearing tests do more than check if you can hear well. They give
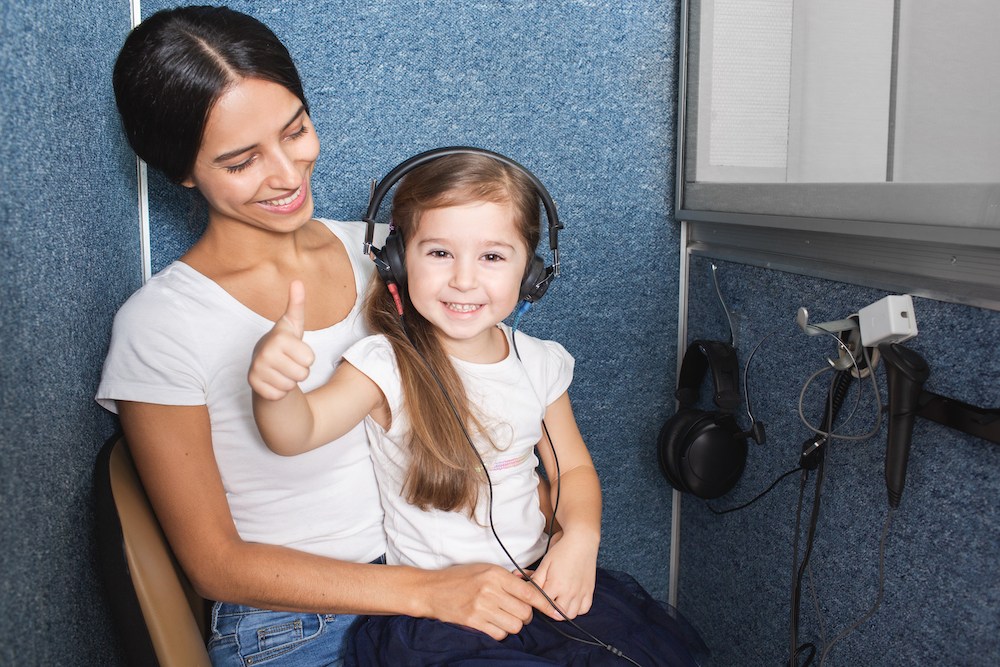
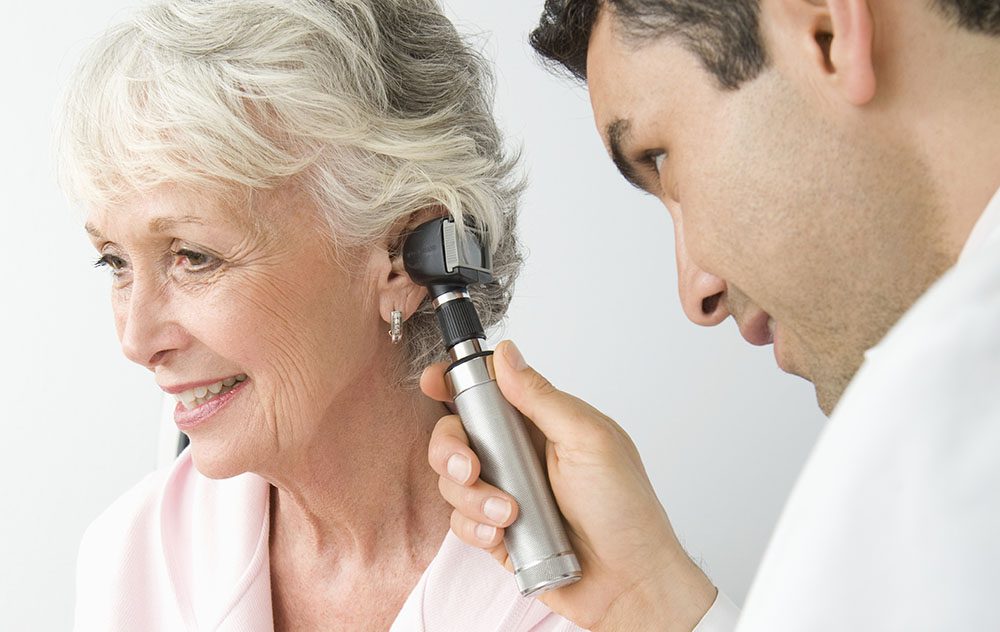

Regular hearing tests do more than check if you can hear well. They give
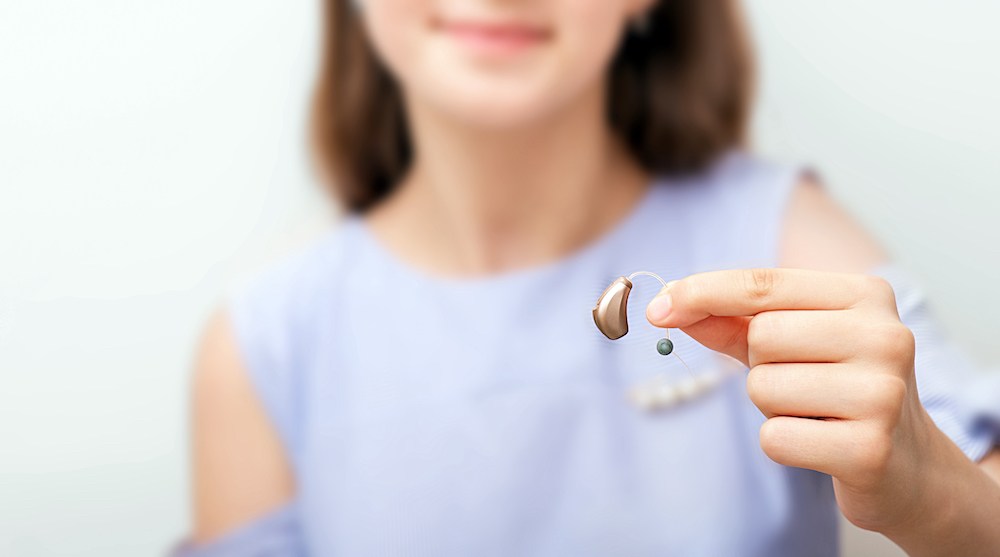

If you wear hearing aids, you know how much they help you during
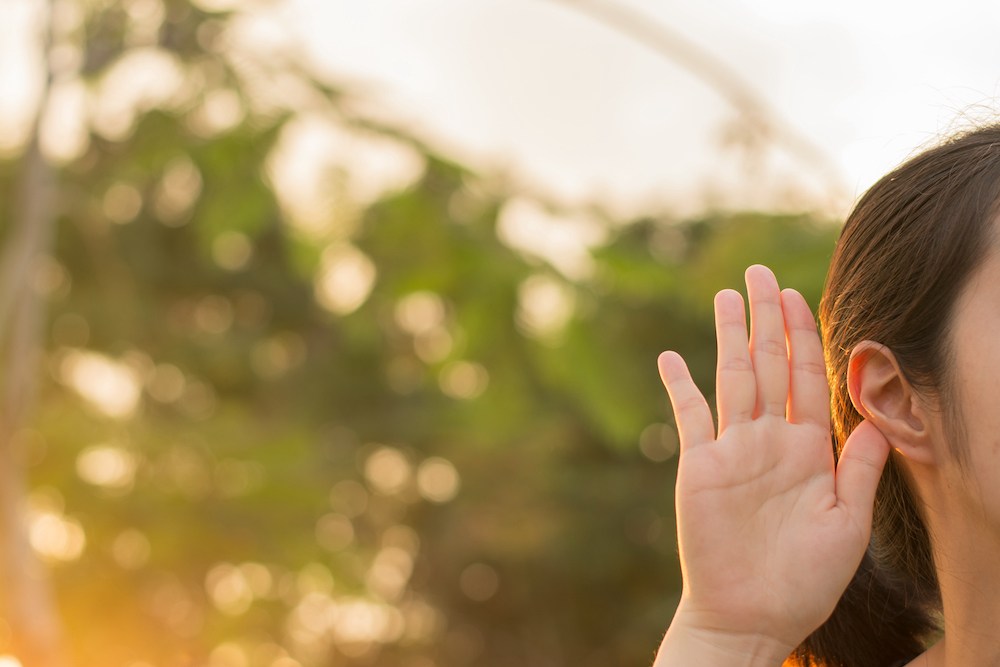

When hearing becomes difficult, the ripple effects touch everyone around